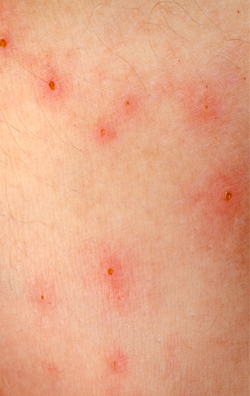
Acne is a common skin problem known as pimples, which appear on the skin with blackhead, white head, papules, nodules and eventually scarring in most of the cases. Acne occurs following blockade of the hair follicles by oil (sebum) and dead cells of the skin. The lesions usually appear on face, neck, upper chest and back area.
This condition is more common in adolescent age group and tends to disappear usually by 25 years of age. However in some people acne may persist even in thirties, forties even fifties.
Other than permanent scarring at the site of lesion, these lesions are quite distressing for the affected person as they heal very slowly and new lesions appear even if the old lesions are there. Different treatment options are available for treating acne; these are benzoyl peroxide, retinoids, antibiotics, salicylic acid etc.
Symptoms
Common presenting symptoms of acne include appearance of lesions mainly in the face, neck, chest and back area as in these areas the oil glands are the most active.
There are mainly two forms of acne, these are
- Non-inflammatory lesions (comedones): these are also known as black and white heads. Actually whenever the openings of the hair follicles are blocked by sebum, dead cells and bacteria comedones appear. If the comedones are open at the surface, they appear black and hence known as blackheads however closed comedones appear skin colored bumps hence known as whitehead
- Inflammatory lesions: these include
1) Papules: characterized by tiny red and painful bumps on the skin
2) Pustules: characterized by pus filled papules
3) Nodules : characterized by large painful lesions beneath the skin
4) Cysts : these lesions look like boils and are more prone to scar formation
Acne usually does not require any medical attention however to prevent repeated attacks of acne and scarring of the already present lesion dermatologist can be consulted.
Causes
There are mainly three factors which play important role in acne production. These are excessive secretion of skin oil (sebum), bacteria accumulation and irritation of the skin mainly due to excessive shedding of skin cells especially at an irregular rate.
Normally the skin remains lubricated by the oil (sebum) produced by the oil glands (sebaceous glands) of the body. The sebum then travels through the hair shaft to the upper part of the skin and appears on the skin surface through the openings of the hair follicles. Whenever there is secretion of excess sebum and shedding off more dead cells, these combine together, blocks the hair follicles and a makes the surroundings favorable for the bacteria thriving.
There are certain factors which can precipitate acne lesions, these are
- Change in hormone production: during puberty both in boys and in girls androgen secretion is increased which stimulate the sebaceous gland to produce excessive sebum which in turn may lead to clogging of the hair follicle. Sometimes pregnancy and regular intake of oral contraceptive pills may lead to the same outcome.
- Intake of specific drugs like corticosteroids, lithium, hormones may increase attack of acne
- Consuming certain food: food rich in carbohydrate tend to increase the blood sugar and the chance of suffering from acne.
Treatment
The aim of acne treatment is reducing sebum production, hastening skin cell division, combating bacterial infection and controlling inflammation.
Usually treatment is done by drugs like benzoyl peroxide, retinoic acid, adapelene etc .Treatment options like chemical peeling, dermabrasion,laser etc are there to reduce the resultant scarring.